Factors Impacting Farm Growth
There are numerous reasons why a farm may want to expand including the following: reduce per-unit costs, improve profit margins, improve asset utilization, bring in new family members, invest retained earnings, and more fully utilize the skills of key managers (Boehlje and Langemeier, 2016). In general, larger businesses have lower per-unit costs, higher profit margins, and are able to more fully utilize assets such as machinery and buildings, which improves their asset turnover ratio. Larger businesses also tend to retain more money in the business. Langemeier and Mintert (2023) noted that farm operators that expect to grow are relatively more optimistic about current and future prospects for production agriculture than operators who expect their farm’s size to remain unchanged or decline. In addition to these factors, farm growth may also be influenced by farm goals and characteristics.
A recent survey of 400 U.S. producers was conducted in late February 2025 to assess individual farm goals, producer sentiment, farm growth, succession plans, sustainability and risk preferences, resilience, and adoption of conservation practices. A previous article focused on farm goals and their tradeoffs (Langemeier, 2025). This article focuses on the relationship between farm growth, farm goals, producer sentiment, and farm characteristics.
Survey Results Pertaining to Farm Growth
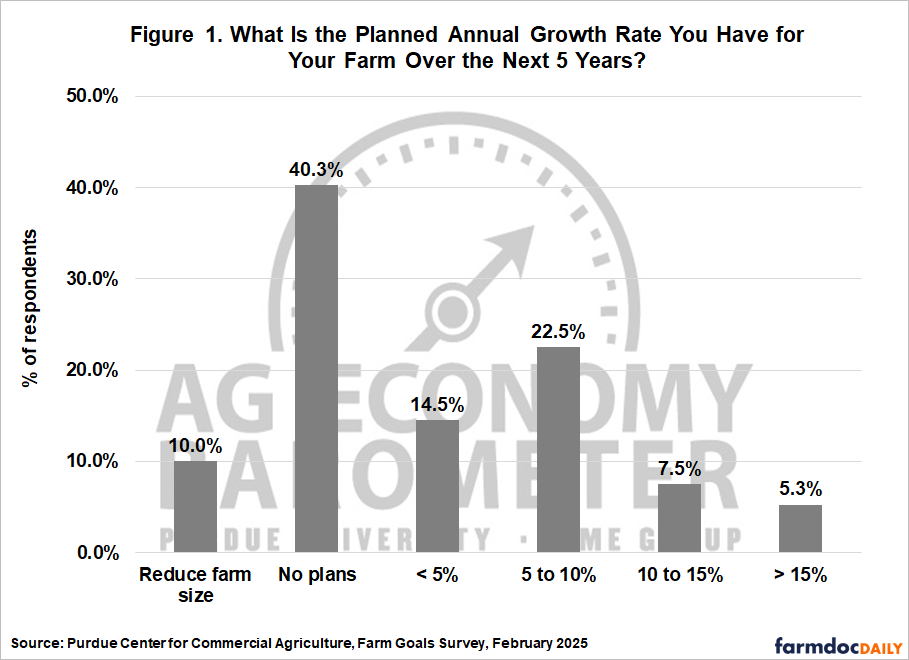
Survey respondents were asked what annual growth rate they expected for their farm over the next five years. The results for this question can be found in Figure 1. Approximately 50% of the survey respondents said that their farm either had “no plans to grow” (40%) or “plan to exit or retire (10%). Respondents who expect their farm to grow “less than 5% annually” or “from 5 to 10% annually” represented 14% and 22% of the total respondents, respectively. The percentage of respondents who expect their farm to grow 10% or more represented approximately 13% of the respondents. A farm that expects to grow 10% every year would double in size every 7 years.
Farm Growth and Farm Goals
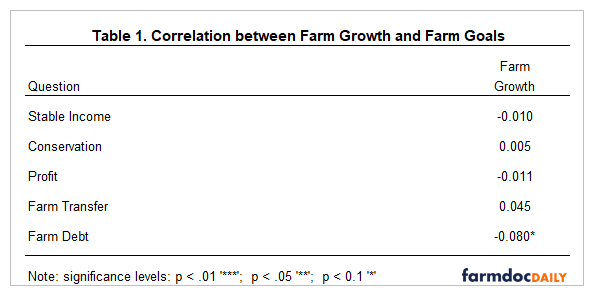
Table 1 presents the correlations between farm growth and each farm goal. Statistical significance is indicated by asterisks. Unlike all other farm goals; farm growth was significant and negatively related to the farm debt goal. This goal was worded as follows: reduce farm debt over time. The negative relationship between farm growth and reduction in debt suggests that those that want to reduce debt realize that doing so is going to limit their ability to expand their operation. We would like to make two additional points about this relationship. First, it is important to point out that reducing leverage often results in a reduction in both risk and expected net returns. Conversely, increasing leverage increases both risk and expected net returns. Thus, lower leverage levels are often related to the risk aversion of the farm operators. Second, operators in the same operation may think differently about this goal. Let’s assume that a farm is managed by a younger operator and an older operator (e.g., father and son). The younger operator may want to borrow money so that the farm can expand more rapidly while the older operator is worried about the risk associated with borrowing more money. Multigenerational operations have to navigate these different preferences.
Farm Growth and Producer Sentiment
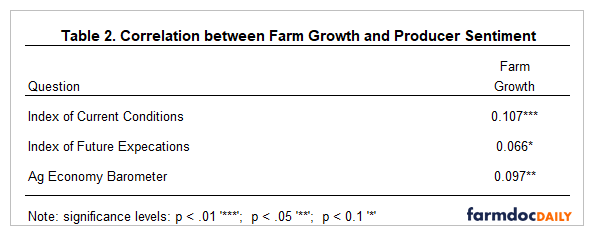
Table 2 presents the relationship between farm growth and three producer sentiment indices: Index of Current Conditions (ICC), Index of Future Expectations (IFE), and the Ag Economy Barometer (AEB). Farm growth was positive and significantly related to ICC, IFE, and AEB. Thus, farm operations that expect to expand more rapidly are more optimistic. These results are consistent with the findings by Langemeier and Mintert (2023). Optimism is likely related to a farm’s financial prospects and whether a farm plans on adding at least one family member to the operation in the next few years. The later point will be discussed further below.
Farm Growth and Farm Characteristics
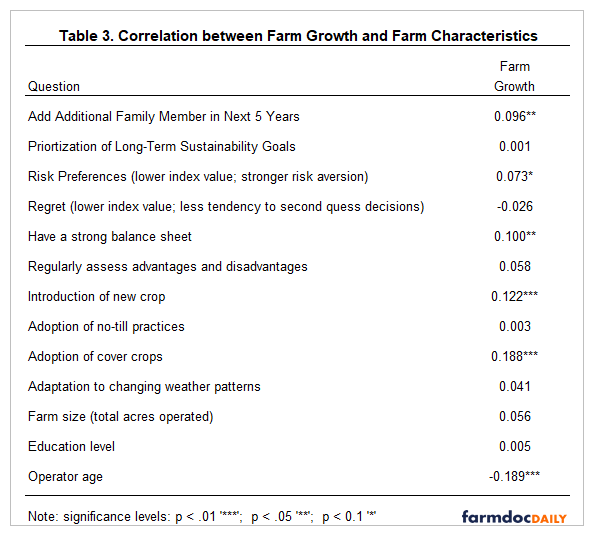
Correlations between farm growth and selected farm characteristics are displayed in Table 3. Significant and positive correlations were found between farm growth and the following variables: adding an additional family member in the next 5 years, risk aversion, having a strong balance sheet, the introduction of a new crop, and the adoption of cover crops. A significant and negative correlation was found between farm growth and operator age. In general, we would expect farms that are planning on adding at least one additional member to have more aggressive plans with regard to farm growth. The correlation coefficient between farm growth and risk preferences suggests that farms that are interested in growing are less risk averse. Farms with a strong balance sheet are in a more solid position for expansion. Farms with more aggressive expansion plans and younger operators are more likely to adopt new practices or technologies such as the introduction of a new crop or cover crops.
Conclusions
This article presents results from a recent survey pertaining to farm goals, and discusses the relationships between farm growth, farm goals, producer sentiment, and farm characteristics. Consistent with previous surveys, only about 50% of the sample of farms are expected to grow in the next 5 years. Of the remaining 50%, 40% expect to remain the same size and 10% expect to reduce the size of their farm. Farms that had a goal to reduce debt over time expected to grow at a slower pace than other farms. Farm growth was positively related to producer sentiment, adding a family member to the operation, a strong balance sheet, and the adoption of new practices, and negatively related to operator age. Moreover, a willingness to take on risk was positively associated with farm growth.
References
Boehlje, M. and M. Langemeier. "Farm Growth: Challenges and Opportunities." farmdoc daily (6):148, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, August 5, 2016.
Langemeier, M. "Farm Goals." farmdoc daily (15):134, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, July 23, 2025.
Langemeier, M. and J. Mintert. "Producer Sentiment and Farm Growth." farmdoc daily (13):82, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, May 5, 2023.
Disclaimer: We request all readers, electronic media and others follow our citation guidelines when re-posting articles from farmdoc daily. Guidelines are available here. The farmdoc daily website falls under University of Illinois copyright and intellectual property rights. For a detailed statement, please see the University of Illinois Copyright Information and Policies here.