Trends in Corn Plant Populations
Trends in seed costs are driven by both changes in seed prices and changes in corn plant populations. This article examines trends in corn plant populations in Iowa, Illinois, and Indiana. In addition, this article examines the proportion of seed costs per acre that are explained by changes in seed prices and plant populations. FINBIN data was used to represent seed cost per acre. Seed price and corn plant population data were obtained from USDA-NASS.
Corn Plant Populations
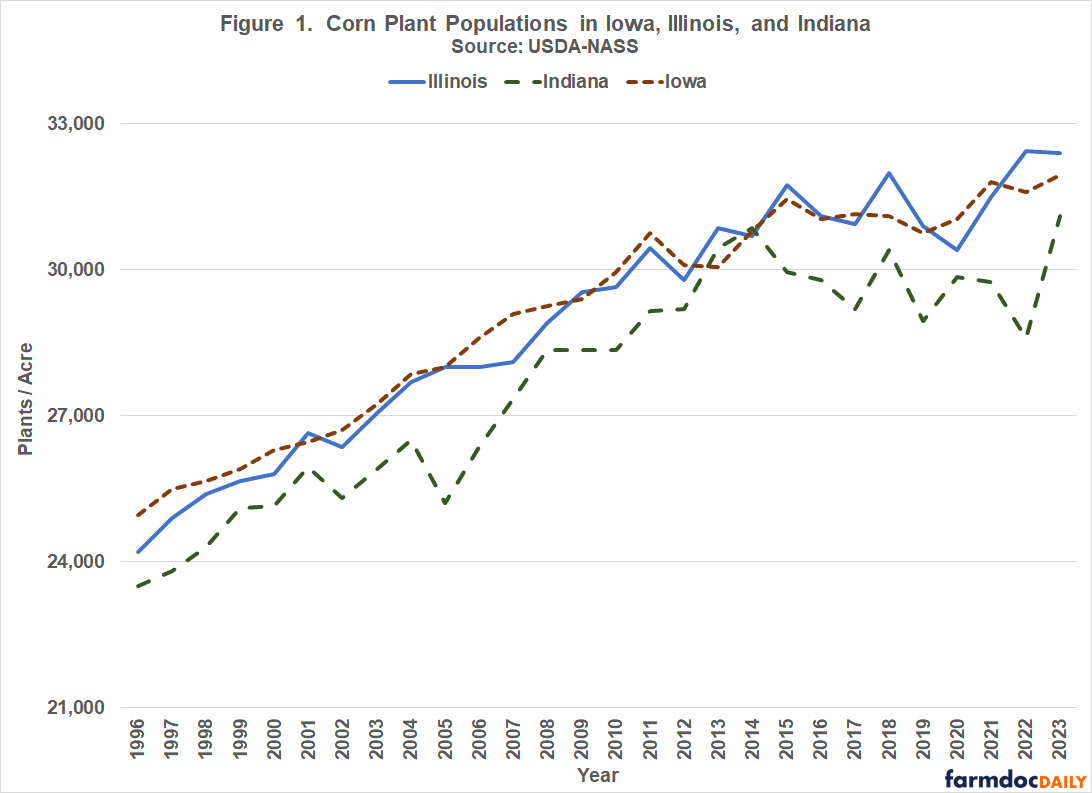
Figure 1 presents corn plant populations in Iowa, Illinois, and Indiana from 1996 to 2023. The annual growth rate in plant populations ranged from 0.91 percent in Iowa to 1.02 percent in Illinois over the study period. Annual increases in plant populations ranged from 256 plants per acre in Indiana to 291 plants per acre in Illinois.
The three trends lines illustrated in Figure 1 are highly correlated, but obviously are not identical. In 1996, the corn plant population in Iowa, Illinois, and Indiana were 24,950; 24,200; and 23,500 plants per acre; respectively. Projected plant populations in 2024 are 32,881 in Iowa, 33,183 in Illinois, and 31,456 in Indiana.
Relationship between Seed Cost, Seed Prices, and Plant Populations
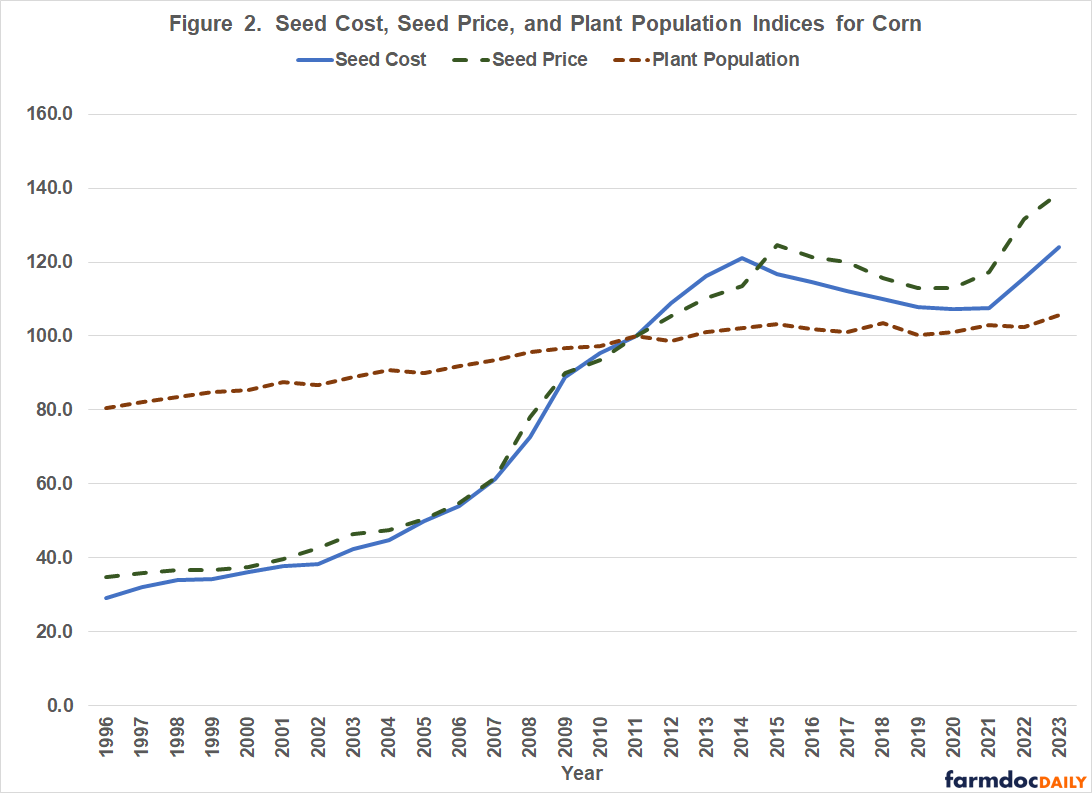
To examine the relative importance of changes in seed price and plant population to changes in seed costs, we developed indices for all three of these measures. Figure 2 presents indices for seed cost, seed price, and plant population in the three states represented in Figure 1 (i.e., Iowa, Illinois, and Indiana) from 1996 to 2023. The base year for each measure was 2011.
It is obvious from Figure 2 that there is a closer link between the seed cost and the seed price indices than there is between these two indices and the plant population index. To examine the relationship between the three measures, we regressed the seed price and plant population indices on the seed cost index. The regression coefficients for both the seed price index and the plant population index were significant. Results indicated that a 1 percent change in the seed price index resulted in a 0.835 percent change in the seed cost index, while a 1 percent change in the plant population resulted in a 1.23 percent change in the seed cost index. Though the seed cost index was more sensitive to changes in plant population, given the relatively larger change in the seed price index during the study period, as illustrated in Figure 2, the seed price index had a larger impact on the seed cost index over the study period. To more fully understand the impact of the seed price index and the plant population index on seed costs, we computed coefficients of separate determination (Langemeier et al., 1992). These coefficients can be used to measure the influence of each independent variable upon the dependent variable. The sum of the coefficients of determination for each variable equal the R-square goodness of fit measure, which was 0.983 for the seed cost regression. Seed price explained approximately 78.2 percent of the variation in seed cost and plant population explained approximately 20.1 percent of the variation.
Concluding Comments
This article discussed trends in corn plant populations for three Corn Belt states, and examined the relationship between seed cost, seed price, and plant populations for corn. Plant populations for corn increased approximately 1 percent per year for Iowa, Illinois, and Indiana from 1996 to 2023. For Illinois, the state with highest projected plant population in 2024, corn plant population increased from 24,200 plants per acre in 1996 to 32,400 plants per acre in 2023. A vast majority of the change in seed costs since 1996 can be explained by changes in seed prices. However, approximately 20 percent of the variation in seed costs since 1996 was explained by changes in corn plant population. Thus, when developing crop budgets, it is important to account for current seed prices and trends in corn plant population in seed cost estimates.
Obviously, increases in corn plant populations have also impacted trends in corn yield since 1996. Though an important topic, it was beyond the scope of this short article to examine the relationship between corn plant population and corn yield. We will leave this topic for a future article.
References
Center for Farm Financial Management, University of Minnesota, FINBIN web site, accessed on April 24, 2024. https://finbin.umn.edu/
Langemeier, M., T. Schroeder, and J. Mintert. “Determinants of Cattle Finishing Profitability.” Southern Journal of Agricultural Economics. 24(December 1992):41-47.
USDA-NASS. Quick Stats, accessed on April 24, 2024. https://quickstats.nass.usda.gov/
Disclaimer: We request all readers, electronic media and others follow our citation guidelines when re-posting articles from farmdoc daily. Guidelines are available here. The farmdoc daily website falls under University of Illinois copyright and intellectual property rights. For a detailed statement, please see the University of Illinois Copyright Information and Policies here.