2015 ARC-CO Payment Estimates for Corn and Soybeans
On February 18th, the National Ag Statistics Service (NASS) released county yield data for the 2015 crop year. This post uses the NASS county yields and current MYA price projections from the USDA to estimate 2015 payments for the Ag Risk Coverage county level program (ARC-CO). Note that the final yields and prices used to determine actual payment levels will differ from the values these payment estimates are based upon. The final MYA price for corn and soybeans will not be known until the marketing year ends in August, and the final yields FSA will use to determine ARC-CO payments will likely not be released until September. See the farmdoc daily article from December 1, 2015 for a more detailed discussion and comparison of NASS county yields and FSA county yields used for the ARC-CO program.
Current MYA Price Projections
The midpoint of the February WASDE range for the 2015/16 MYA corn price is $3.60 (range of $3.35 to $3.85). This is 32% below the 2015 ARC program benchmark price of $5.29. Since the ARC-CO program provides a guarantee equal to 86% of the county’s benchmark revenue, the projected corn price implies that the actual corn yield in a county can be up to 26% higher than the ARC benchmark yield to trigger a payment. For soybeans, the midpoint of the WASDE range is $8.80 (range of $8.05 to $9.55). This implies that the actual soybean yield in a county can be up to 20% above the 2015 benchmark yield to trigger an ARC-CO payment on soybean base. Counties where actual corn (soybean) yields are up to 11.7% (6%) above the benchmark yield for 2015 will trigger the maximum ARC-CO payment, which equals 10% of the county benchmark revenue.
Estimated ARC-CO Payments for Corn and Soybeans
Figure 1 illustrates estimated 2015 ARC-CO payments on corn base acres. The county yield data from NASS covers only a portion of the counties in the US where ARC-CO is available for corn. More than 70% of the counties in the US where a NASS yield was published are estimated to trigger an ARC-CO payment for corn base in 2015, with over 40% of those counties triggering the maximum payment equal to 10% of the county revenue benchmark.

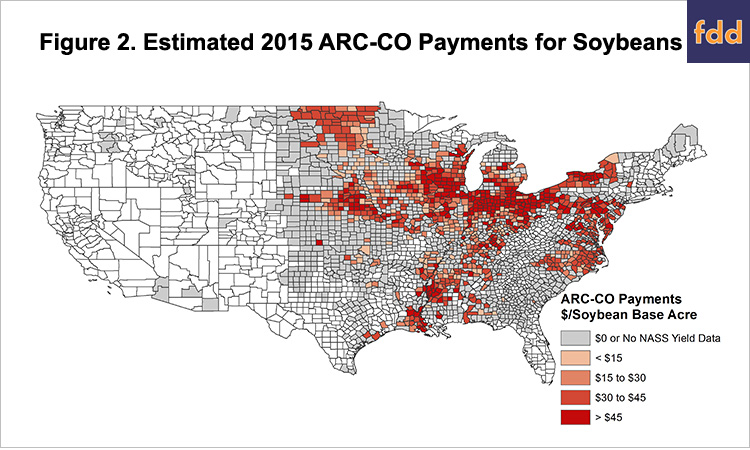
Figure 2 shows estimated 2015 ARC-CO payments on soybean base acres. Again, NASS reported a county yield for only a portion of the counties with the ARC-CO program for soybeans. ARC-CO payments are estimated to be triggered on over 60% of counties with a NASS soybean yield reported, with more than 30% of counties triggering the maximum payment on soybean base acres.
Estimated ARC-CO Payments in Illinois
In Illinois the average estimated ARC-CO payment on corn base is over $65 per base acre. County level payment estimates for Illinois are illustrated in Figure 3. Payments would be triggered in over 90% of Illinois counties, and the maximum payment would be triggered for corn in roughly 2/3 of Illinois counties. Only three counties with a corn yield reported by NASS in Illinois for 2015 would not receive a payment at the current price projection of $3.60. These counties, shown in white in Figure 3, are Monroe, Piatt, and Pope. NASS reported county yield averages well above the benchmark yield levels in all three of these counties.

Adjusting the projected MYA price for corn to the high end of the WASDE range ($3.85) would still result in ARC-CO payments on corn base averaging over $45 per base acre across the state, with more than 75% of counties triggering payments and just over 25% of counties triggering the maximum payment.
The average estimated ARC-CO payment on soybean base in Illinois is just over $28 per base acre. Payments would be triggered in more than 70% of Illinois counties, with more than 15% of counties triggering the maximum payment. A handful of counties, located mainly in southern and east central Illinois, had reported NASS yields which were high enough to result in a zero ARC-CO payment estimate on soybean base.
Increasing the projected MYA price for soybeans to the higher end of the WASDE range ($9.55) lowers the average ARC-CO payment estimate to $6.60 per base acre with less than 40% of counties triggering a payment, and no counties triggering the maximum payment on soybean base acres.

Summary
Despite corn and soybean yields which generally above average in most areas in 2015, low price levels projected for corn and soybeans for the 2015/16 marketing year make ARC-CO payments for both crops likely across much of the US. Using county yields released by NASS last week, payments for ARC-CO were estimated at the midpoint of the price range in the February WASDE report for corn and soybeans. Using these yields and price levels, a large proportion of counties are expected to trigger 2015 ARC-CO payments for corn and soybeans, with a significant number of counties hitting the maximum payment level of 10% of the county benchmark revenue.
In Illinois, the ARC-CO payment for corn is estimated to average over $65 per base acre with only three counties not expected to receive a payment. For soybeans, the average ARC-CO payment estimate is just over $28 per base acre in Illinois, again with the majority of counties expected to receive some payment.
2015 ARC-CO payments are only provided as estimates at this time. The final yields used in calculating payments can differ from the yields released by NASS, and will also cover additional counties in the US. The final MYA price levels for corn and soybeans will not be known with certainty until the marketing year ends in August. However, where NASS yields are available, estimates for the 2015 ARC-CO payment levels can be helpful for planning purposes.
References
Schnitkey, G. "FSA Yields Used in Computing ARC-CO Payments Compared to NASS Yields." farmdoc daily (5):222, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, December 1, 2015.
Disclaimer: We request all readers, electronic media and others follow our citation guidelines when re-posting articles from farmdoc daily. Guidelines are available here. The farmdoc daily website falls under University of Illinois copyright and intellectual property rights. For a detailed statement, please see the University of Illinois Copyright Information and Policies here.







