The Accuracy of Early Season Crop Weather Model Forecasts of the U.S. Average Corn Yield
Corn yield forecasts contained in May, June, and July WASDE reports from the USDA provide important information to market participants. The forecasts are based on crop weather models developed and maintained by the World Agricultural Outlook Board (WAOB). In a recent farmdoc daily article (July 2, 2020), we described the WAOB crop weather model for corn and replicated the generation of 2020 yield forecasts. We also specified an alternative crop weather model for corn in this farmdoc daily article (June 25, 2020) and used the model to generate 2020 trend yield projections for corn based on different sample periods. The purpose of today’s article is to evaluate the accuracy of these crop weather models for making early season forecasts of the U.S. average yield of corn. This extends the evaluation of WAOB early season accuracy of corn yield forecasts found in this farmdoc daily article (April 30, 2015).
Analysis
We begin by describing the WAOB crop weather model used to generate WASDE corn yield forecasts in May through July each year. As detailed in Westcott and Jewison (2013), the WAOB crop weather model is a “Thompson-style” regression model. Specifically, the model of U.S. average corn yield was originally estimated using data for 1988 through 2012 and includes the following explanatory variables: i) a time trend variable to represent technological change, ii) corn planting progress as of May 15th, iii) June precipitation shortfall, iv) July precipitation, and v) July average temperature. The planting progress and weather data were collected for eight key corn-producing States (Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, Missouri, Minnesota, South Dakota, and Nebraska). An aggregate measure for the eight states was constructed using harvested corn acres to weight state-specific observations.
The mid-May planting progress variable was based on data in the weekly Crop Progress report from the USDA and is interpolated to May 15th using adjacent weeks in years when planting progress was not reported for that specific date. Since extreme weather deviations from normal in June can have large impacts, as seen in 2012 and in 1988, the model uses a measure of the June precipitation shortfall from average in years when June precipitation is in the lowest 10-percent tail of its historical distribution. Because much of corn reproduction occurs in July, both temperature and precipitation from that month were included in the model.
Our objective is to conduct an “out-of-sample” forecasting exercise using the WAOB crop weather model over 2013-2019. We start the evaluation in 2013 since this is the first year that the WAOB model was used to generate early season corn yield projections. Since published WASDE corn and yield forecasts for May, June, and July are based on the crop weather model, we collected the corn yield forecasts published in these years. Even though WASDE yield forecasts are switched to NASS survey-based estimates in August, we thought it would be interesting to also assess the forecasting performance of the WAOB model in August. To do this, we had to compute the August forecasts using the following procedure:
- Estimate the crop weather model coefficients using data from 1988-2012.
- Compute August 2013 forecasts by plugging in actual values for trend, planting progress, June precipitation shortfall, July precipitation, and July temperature for 2013.
- Repeat the process by adding one year to the estimation sample period and compute August forecasts for the following year.
Panel A of Table 1 contains the WAOB crop weather model forecasts for May-August over 2013-2019, along with the NASS August forecast and the USDA final yield estimate each year. We include NASS yield forecasts for August, as these are considered the “gold-standard” when projecting corn yields. In addition, we report the WAOB model forecasts for May-July 2020. We could not compute the August 2020 WAOB model forecast because we do not yet have access to the June and July weather data for 2020. The early season WAOB model forecasts start at 158 bushels per acre in May 2013 and increase to 178.5 bushels per acre in May 2020. The 20.5 bushel increase in forecasts over this period represents an average increase in yield forecasts of 2.6 bushels per year. Note that in most years the published WAOB yield forecast is the same during May-July, which makes sense when planting progress comes in near the historical average and the June precipitation shortfall is zero.

Panel B of Table 1 contains the WAOB yield forecast errors for May-August over 2013-2019. The errors are computed by subtracting the forecasts found in Panel A from the final USDA estimates, also found in Panel A. Of course, 2020 errors cannot be computed because final yield is not yet available. The accuracy record of the WAOB model is mixed, with some May forecasts near the final estimate (2013 and 2015) and some relatively far from the final estimate (2016 and 2019). This is not unexpected for early season forecasts, as key weather information is not yet available. It is interesting to observe that all but one of the forecast errors in May-July are positive, which implies that the WAOB model under-estimated the final corn yield. The mean errors (ME) presented at the bottom of Table 1 indicate that the average level of under-estimation (bias) ranged from 2.0 bushels in May to 3.6 bushels in June and July. NASS yield forecasts in August also under-estimated on average over 2013-2019, but at 1.3 bushels this was the smallest bias of the forecasts considered in Table 1.
A key measure of forecast accuracy is mean absolute error (MAE), which is simply the average of the absolute value of the forecast errors presented in Panel B of Table 1. This is a measure of how close the forecast comes to the final USDA estimate, irrespective of whether the forecast is too high or too low. The MAE for the WAOB crop weather forecasts over 2013-2019 ranged between 3.6 and 4.4 bushels per acre. In percentage terms, this represents 2.1 to 2.6 percent of the forecast levels reported in Panel A of Table 1, which strikes one as reasonably accurate considering the simplicity of the WAOB crop weather model. Furthermore, this represents an improvement in percentage accuracy compared to the 1993-2014 period, as reported in this earlier farmdoc daily article (April 30, 2015). One should treat this comparison with some caution, however, because of the two very large forecast errors that occurred in 1993 and 2012 due to the historically unusual weather conditions in these two years (floods in 1993 and drought in 2012). Finally, the NASS August yield forecast has the smallest MAE (2.8 bushels) of the forecasts found in Table 1. This is not surprising because NASS forecasts are based on thousands of farm operator and objective yield samples, and one would expect forecasts based on such extensive information to be more accurate.
The next step of the analysis is to generate corn yield forecasts using the alternative crop weather model presented in this farmdoc daily article (June 25, 2020). We are interested whether this alternative crop weather model is more or less accurate than the WAOB model. This crop weather model relates the U.S. average corn yield to a linear trend, late planting, quadratic functions of June and July precipitation, and a linear function of July temperature as explanatory variables. The weather variables are acreage weighted-averages for 10 states in the Corn Belt.
We use the following procedure to generate corn yield forecasts for this alternative crop weather model:
- Estimate the crop weather model coefficients using data from 1988-2012.
- Compute May-August 2013 forecasts by plugging in known variables at the time of the forecast is assumed to be made, and projecting values for the remaining variables. The trend variable is always the index value of the forecast year. When projections are necessary for linear variables (planting progress, July temperature), sample averages over 1988-2012 are used. When projections are necessary for non-linear variables (June and July precipitation), a Monte Carlo simulation is used in order to reflect the quadratic impact on yield forecasts. August forecasts are based on actual values for all variables.
- Repeat the process by adding one year to the estimation sample period and computing May-August forecasts for the following year.
Panel A of Table 2 contains the alternative crop weather model (IH) forecasts for May-August over 2013-20202, along with the NASS August forecast and the USDA final yield estimate each year. We could not compute the July and August 2020 model forecasts because we do not yet have access to the June and July weather data for 2020. The early season IH model forecasts start at 160.9 bushels per acre in May 2013 and increase to 177.3 bushels per acre in May 2020. The 16.4 bushel increase in forecasts over this period represents an average increase in yield forecasts of 2.1 bushels per year. Note that that IH model forecasts differ across months because different combinations of variables are known vs. projected each month.
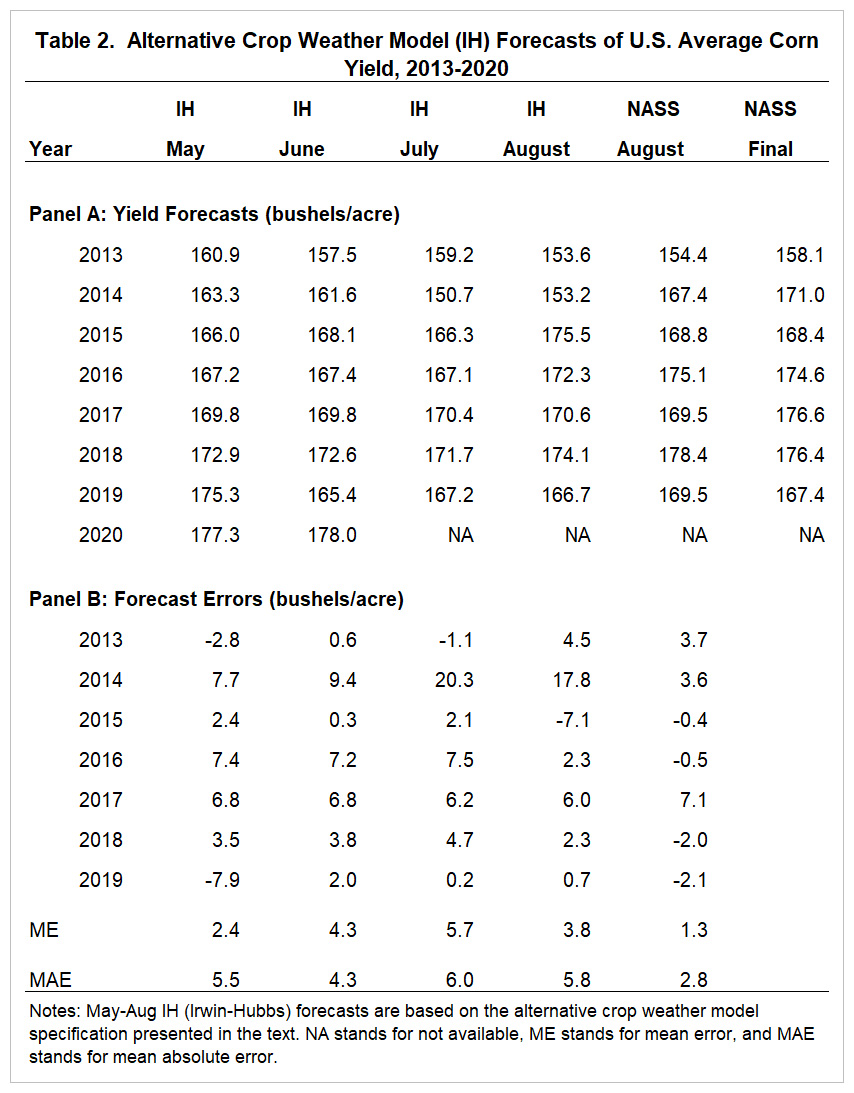
Panel B of Table 2 contains the alternative IH yield forecast errors for May-August over 2013-2019. Once again, the errors are computed by subtracting the forecasts found in Panel A from the final USDA estimates, also found in Panel A. Like the WAOB model, the vast majority of the forecast errors in May-August are positive, which implies that the IH model under-estimated the final corn yield. The mean errors (ME) presented at the bottom of Table 2 indicate that the average level of under-estimation (bias) ranged from 2.4 bushels in May to a whopping 5.7 bushels in July. The high level of bias in July and August forecasts can be directly traced to huge under-estimates of final yield made in 2014. It is interesting to note that the WAOB model did not make nearly as large of an under-estimate in 2014. The reason is the WAOB model is not as sensitive to July precipitation. This was an advantage in 2014 when the very unusual combination of low July precipitation and a new record yield occurred. The mean absolute error of the alternative IH crop weather model ranged from 4.3 to 6.0 bushels per acre. In percentage terms, this represents 2.6 to 3.8 percent of the forecast levels reported in Panel A of Table 2, which is higher than the comparable figures for the WAOB crop weather model.
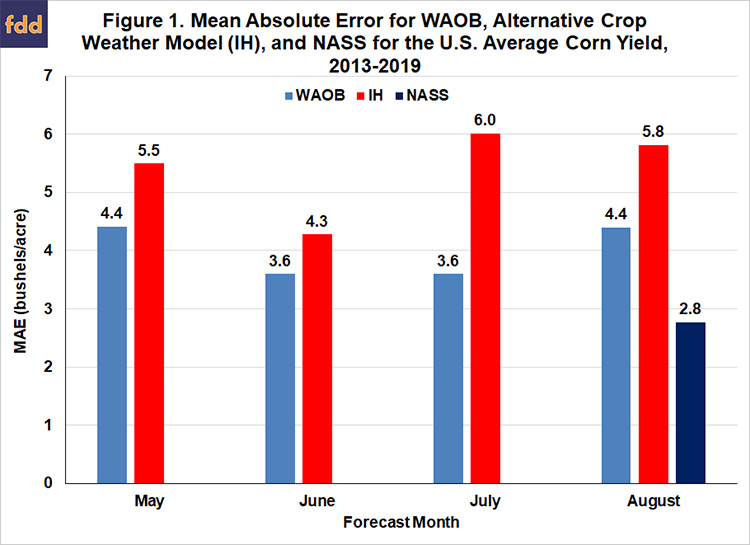
Figure 1 presents the month-by-month mean absolute errors for the WAOB crop weather model, the IH alternative crop weather model, and the NASS forecast in August. Two results stand out. First, the WAOB crop weather model is more accurate in all four months, and by a considerable amount in May, July, and August. Second, the NASS forecast in August is substantially more accurate than either of the crop weather model forecasts. The NASS forecast beats the WAOB model forecasts in August by 1.6 bushels and the IH alternative model by 3.0 bushels. The NASS forecasts are the clear victors in terms of August forecast accuracy.
Implications
Crop weather models are widely used to make early season corn yield forecasts. We examine the accuracy of forecasts from two crop weather models over 2013-2019 in this article. The first is the model developed and maintained by the World Agricultural Outlook Board (WAOB) of the USDA. It is used to generate forecasts for the May, June, and July WASDE reports. The second is an alternative but similar crop weather model that we developed and presented in an earlier farmdoc daily article (June 25, 2020). We find that nearly all of the early season forecasts from the models during this eight-year period were too low, with the bias ranging from about 2 to 6 bushels per acre. In terms of mean absolute forecast error, the WAOB crop weather model was more accurate than our crop weather model in all four months. Consequently, in horse-race terms, the WAOB model is hands down the winner over our alternative model. Finally, the NASS forecast in August is the clear victor in terms of accuracy compared to either crop weather model. It is no wonder then that the August Crop Production report is so highly anticipated.
References
Irwin, S., D. Good and D. Sanders. "Understanding and Evaluating WAOB/USDA Corn Yield Forecasts." farmdoc daily (5):79, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, April 30, 2015.
Irwin, S. and T. Hubbs. "Understanding the WAOB Crop Weather Model for Corn." farmdoc daily (10):121, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, July 2, 2020.
Irwin, S. and T. Hubbs. "Unconditional vs. Conditional Trend Estimates for U.S. Corn and Soybeans." farmdoc daily (10):116, Department of Agricultural and Consumer Economics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, June 25, 2020.
Westcott, P.C., and M. Jewison. "Weather Effects on Expected Corn and Soybean Yields." FDS-13g-01, Economic Research Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture, July 2013. https://www.ers.usda.gov/publications/pub-details/?pubid=36652
Disclaimer: We request all readers, electronic media and others follow our citation guidelines when re-posting articles from farmdoc daily. Guidelines are available here. The farmdoc daily website falls under University of Illinois copyright and intellectual property rights. For a detailed statement, please see the University of Illinois Copyright Information and Policies here.







