Impacts of Removal of Illinois Sales Tax Exemptions on Illinois Grain Farms
Farmers do not pay Illinois’ 6.25% sales tax on exempt agriculture inputs. We examine the impacts removing existing sales tax exemptions resulting in a 6.25% sales tax added to fertilizer, pesticides, seed, and machinery-related expenses. From 2015 to 2019, these sales taxes would have totaled $33,961 on northern Illinois farms and reduced net farm income by 54%. Similar impacts would have occurred on central and southern Illinois farms. The imposition of sales taxes would significantly reduce the profitability of Illinois grain farms.
Tax exemptions
The State of Illinois collects a 6.25% tax on sales. Municipalities and other government bodies may impose additional taxes on sales.
There are three tax exemptions within regulations published by the Illinois Department of Revenue that have direct impacts on Illinois grain farms:
- Farm chemicals (Section 130.1955)
- Seeds and fertilizer (Section 130.2110)
- Farm machinery and equipment (Section 130.305). This exemption applies to purchases and sales of farm machinery, repairs, and machinery hire.
Those above would also apply to livestock production and other forms of agricultural production.
Evaluation of Illinois Grain Farms
The impacts of removing sales tax exemptions on Illinois grain farms were evaluated using Illinois Farm Business Farm Management (FBFM) data for the five years from 2015 to 2019. Net incomes, tillable acres, and expenditures were averaged for the five-years to even out changes in revenues and expenses across time. Results are summarized for farms in:
- Northern Illinois
- Central Illinois with high-productivity farmland (Central-High)
- Central Illinois with lower-productivity farmland (Central-Low)
- Southern Illinois
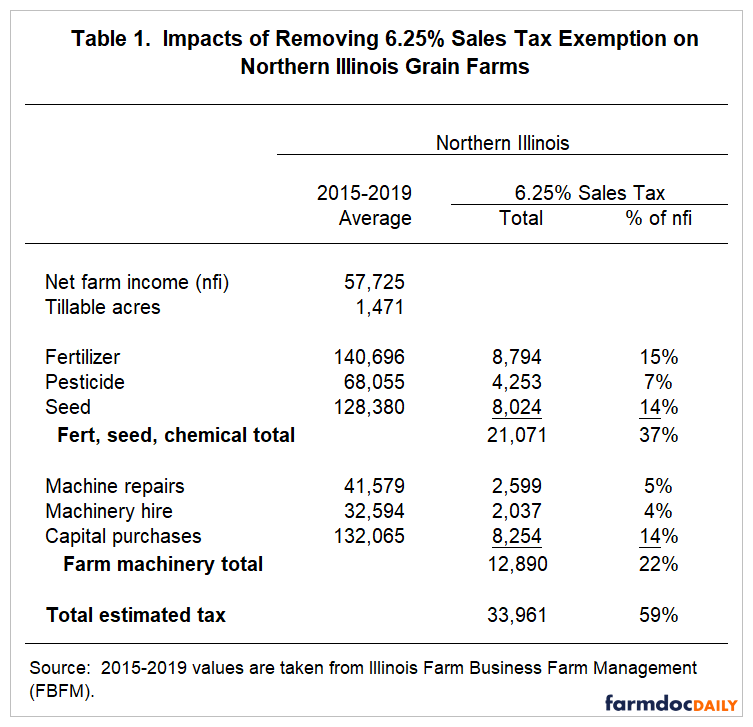
Table 1 shows results for farms in Northern Illinois. From 2019-2019, farms in Northern Illinois had an average net farm income of $57,725 with an average farm size of 1,471 tillable acres. Average expenditures were:
- $140,696 on fertilizer,
- $68,055 on pesticides,
- $128,380 on seed,
- $41,579 on machinery repairs,
- $32,594 on machinery hire,
- $132,065 on capital purchases.
Impacts of Removing the 6.25% Sales Tax Exemption
The Illinois sales tax is 6.25%. There could be municipality sales taxes in addition to the Illinois tax.
A 6.25% sales tax would have resulted in $21,071 per farm on fertilizer, pesticide, and seeds (see Table 1). This sales tax would total 37% of net farm income.
A 6.25% sales tax on farm machinery items would have resulted in $12,890 of sales tax or 18% of net farm income.
The impact of removing both would be $33,961, or 59% of net farm income.
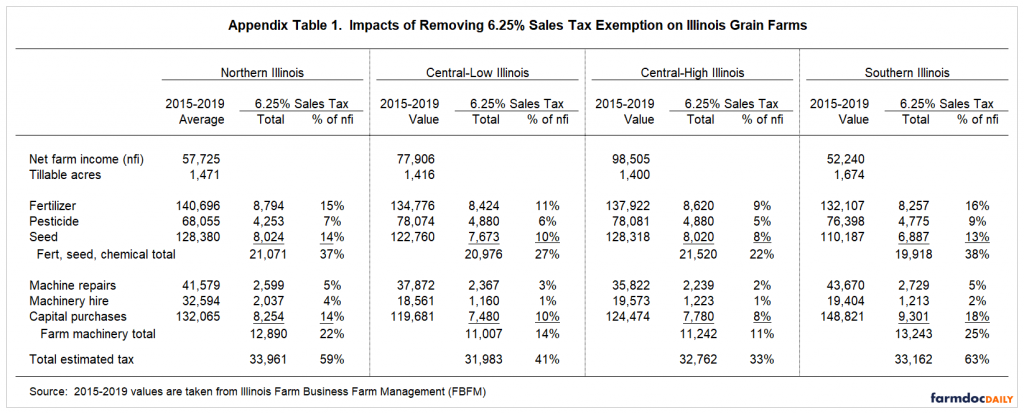
Other regions have roughly similar impacts (see Appendix Table 1). Much of the difference in results across the regions is due to differences in net incomes. Central Illinois had relatively better-growing conditions and higher incomes than northern and southern Illinois.
Caveats
Ways in which the removal of the sales tax exemptions would be implemented are not known. For example, one type of expenses may continue to be tax exempt, while another type of expenditure could be subject to the sales tax. The majority of capital purchases relate to machinery but also include building and land improvements.
Summary
The imposition of a sales tax on currently exempted items would have reduced net farm income by over 50% from 2015 to 2019. While the exemption removal would impact input supply firms and likely change input prices, similar results would occur in the future if a sales tax was imposed on Illinois farmers.
Disclaimer: We request all readers, electronic media and others follow our citation guidelines when re-posting articles from farmdoc daily. Guidelines are available here. The farmdoc daily website falls under University of Illinois copyright and intellectual property rights. For a detailed statement, please see the University of Illinois Copyright Information and Policies here.